Kubernetes Management
Overview
Vapor provides comprehensive Kubernetes cluster management capabilities, allowing you to manage workloads, monitor resources, and deploy applications directly from the web interface. The Kubernetes section integrates seamlessly with your cluster, providing both basic operations and advanced features like Helm chart management.
Accessing Kubernetes Features
Navigate to the Kubernetes section through the sidebar:
Kubernetes
├── Workloads (Pods, Deployments, StatefulSets, etc.)
├── Networks (Services, Ingresses, NetworkPolicies)
├── Storages (PVCs, PVs, StorageClasses)
├── Configurations (ConfigMaps, Secrets)
├── Nodes (Cluster nodes and resources)
├── CRDs (Custom Resource Definitions)
└── Helm Charts (Package management)Workloads Management
Pods
The Pods view provides comprehensive pod management:
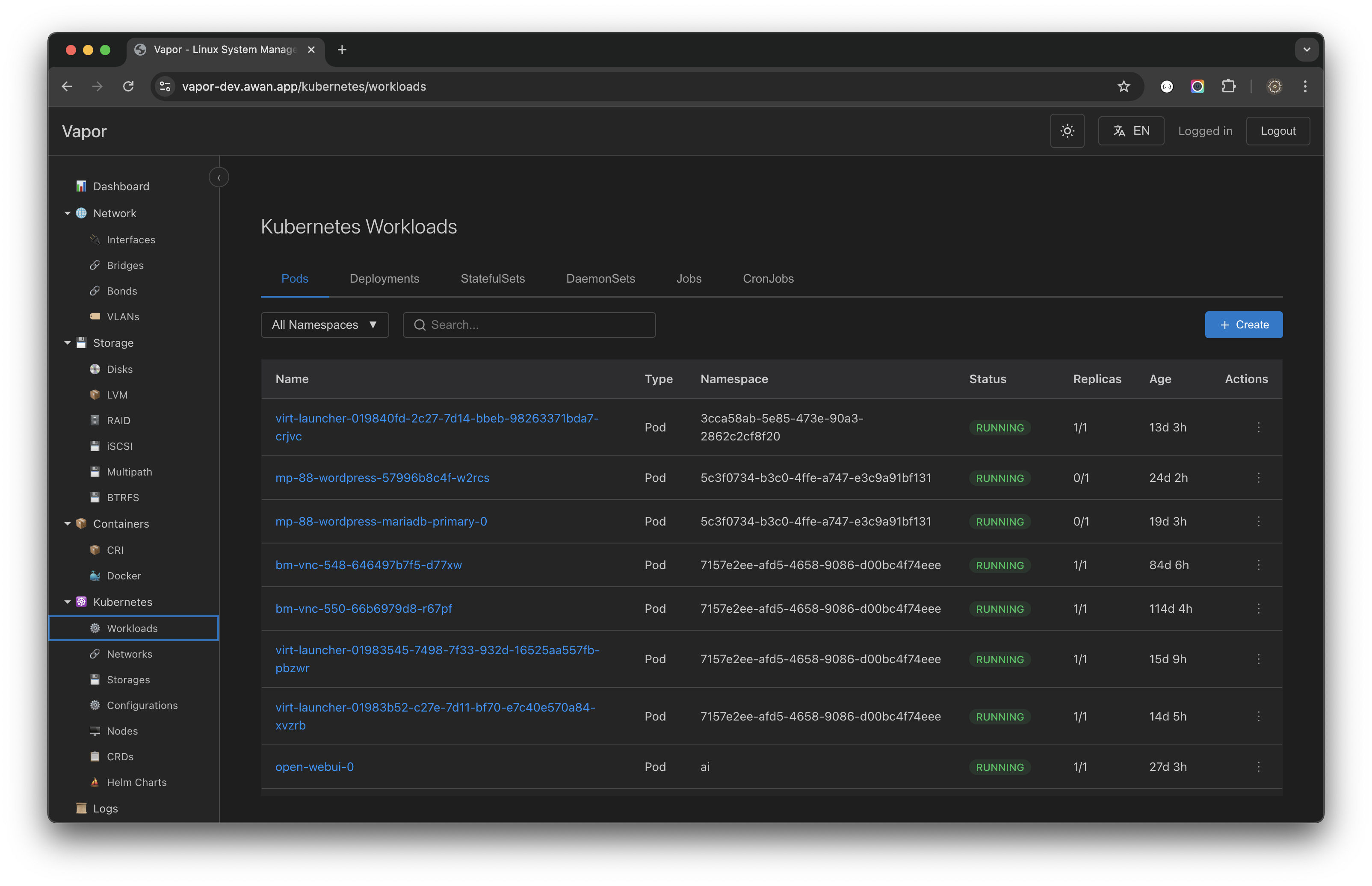
Pod List Features
Namespace Filtering
- Select "All Namespaces" or specific namespace
- Quick namespace switching
- Namespace isolation for security
Search and Filter
- Real-time search by pod name
- Filter by status (Running, Pending, Failed)
- Sort by age, status, or resource usage
Status Indicators
- 🟢 RUNNING: Pod is healthy and running
- 🟡 PENDING: Pod is being scheduled or starting
- 🔴 FAILED: Pod has crashed or failed to start
- 🟠 UNKNOWN: Pod status cannot be determined
Pod Information Display
Each pod entry shows:
- Name: Full pod identifier
- Namespace: Kubernetes namespace
- Status: Current pod state
- Replicas: Number of containers
- Age: Time since creation
- Actions: Quick action menu
Pod Details
Click on any pod to view detailed information:
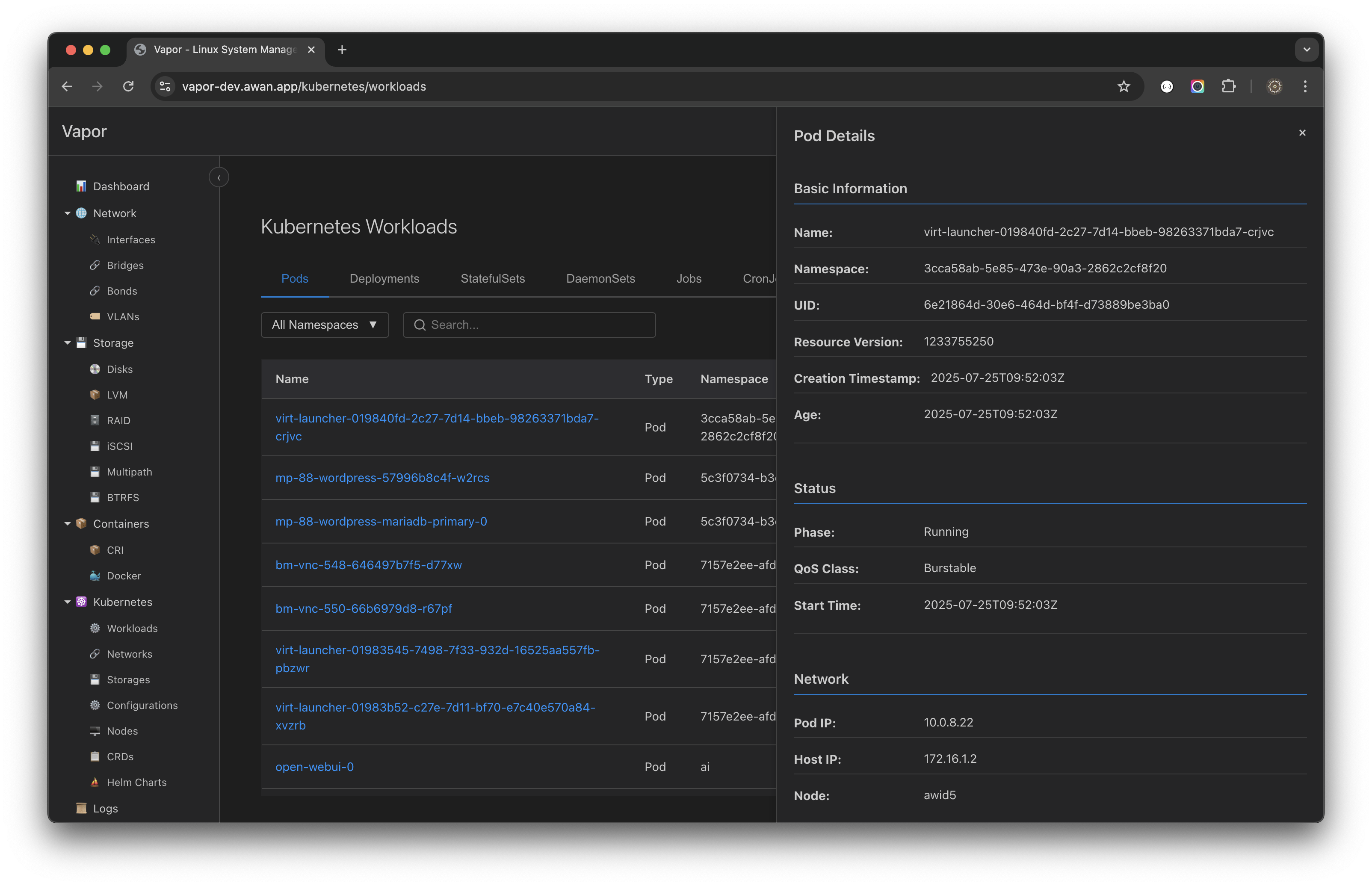
Basic Information
Name: virt-launcher-019840fd-2c27-7d14-bbeb-98263371bda7-cnjvc
Namespace: 3cca58ab-5e85-473e-90a3-2862c2cf8f20
UID: 6e21864d-30e6-464d-bf4f-d73889bc3ba0
Resource Version: 1233755250
Creation Time: 2025-07-25T09:52:03Z
Age: 13 days, 3 hoursStatus Information
Phase: Running
QoS Class: Burstable
Start Time: 2025-07-25T09:52:03ZNetwork Information
Pod IP: 10.0.8.22
Host IP: 172.16.1.2
Node: avid5Creating Resources
Vapor supports creating Kubernetes resources using YAML or JSON:
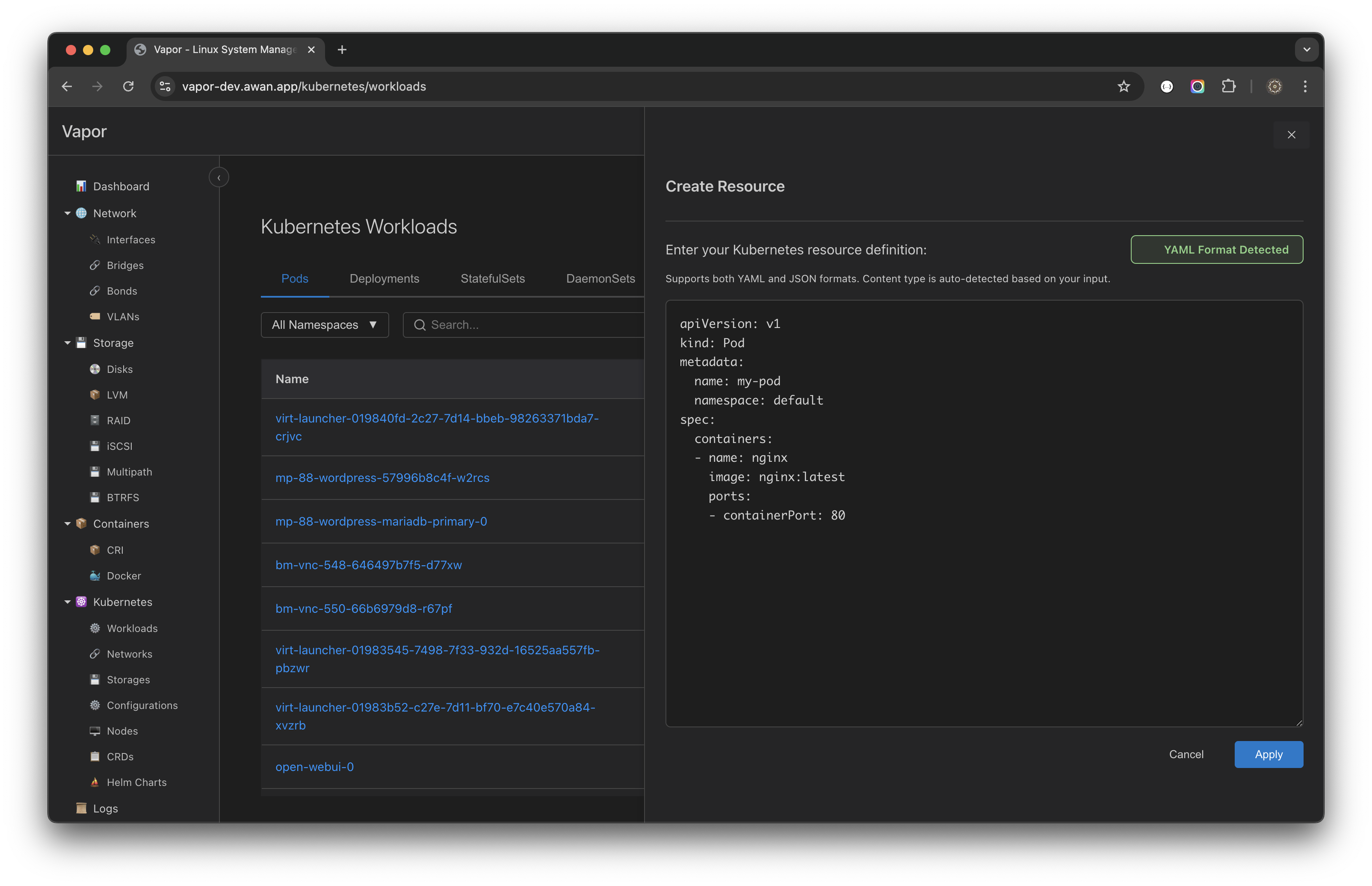
Resource Creation Process
- Click "Create" button in the workloads view
- Enter resource definition in YAML or JSON format
- Format auto-detection identifies the syntax
- Validation occurs before submission
- Apply to create the resource
Example Pod Creation
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: my-pod
namespace: default
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 80Pod Operations
Viewing Logs
Access real-time pod logs:
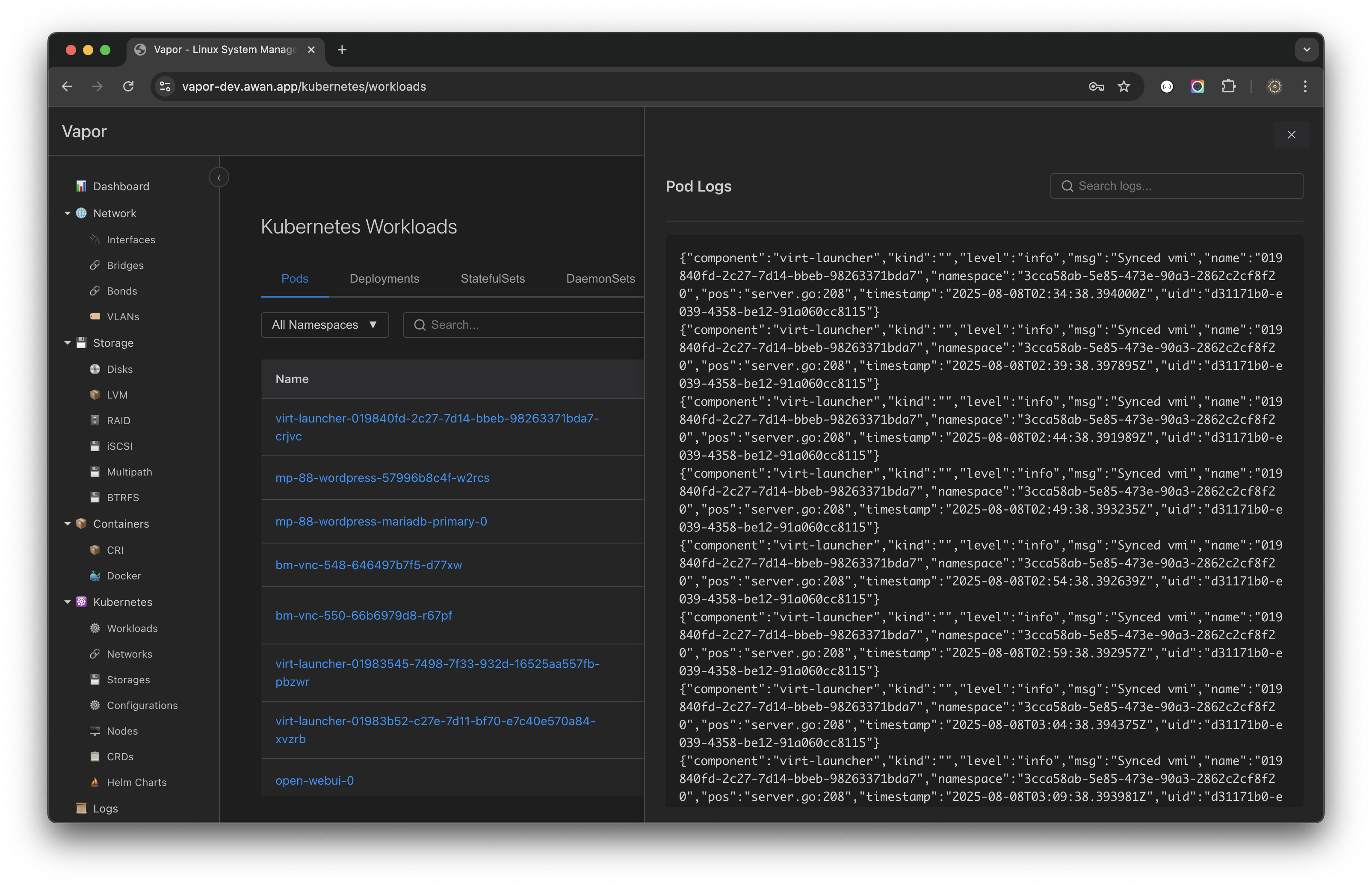
Log Features:
- Real-time streaming
- Search within logs
- Timestamp display
- JSON formatting for structured logs
- Export capabilities
Deleting Pods
Safe deletion with confirmation:
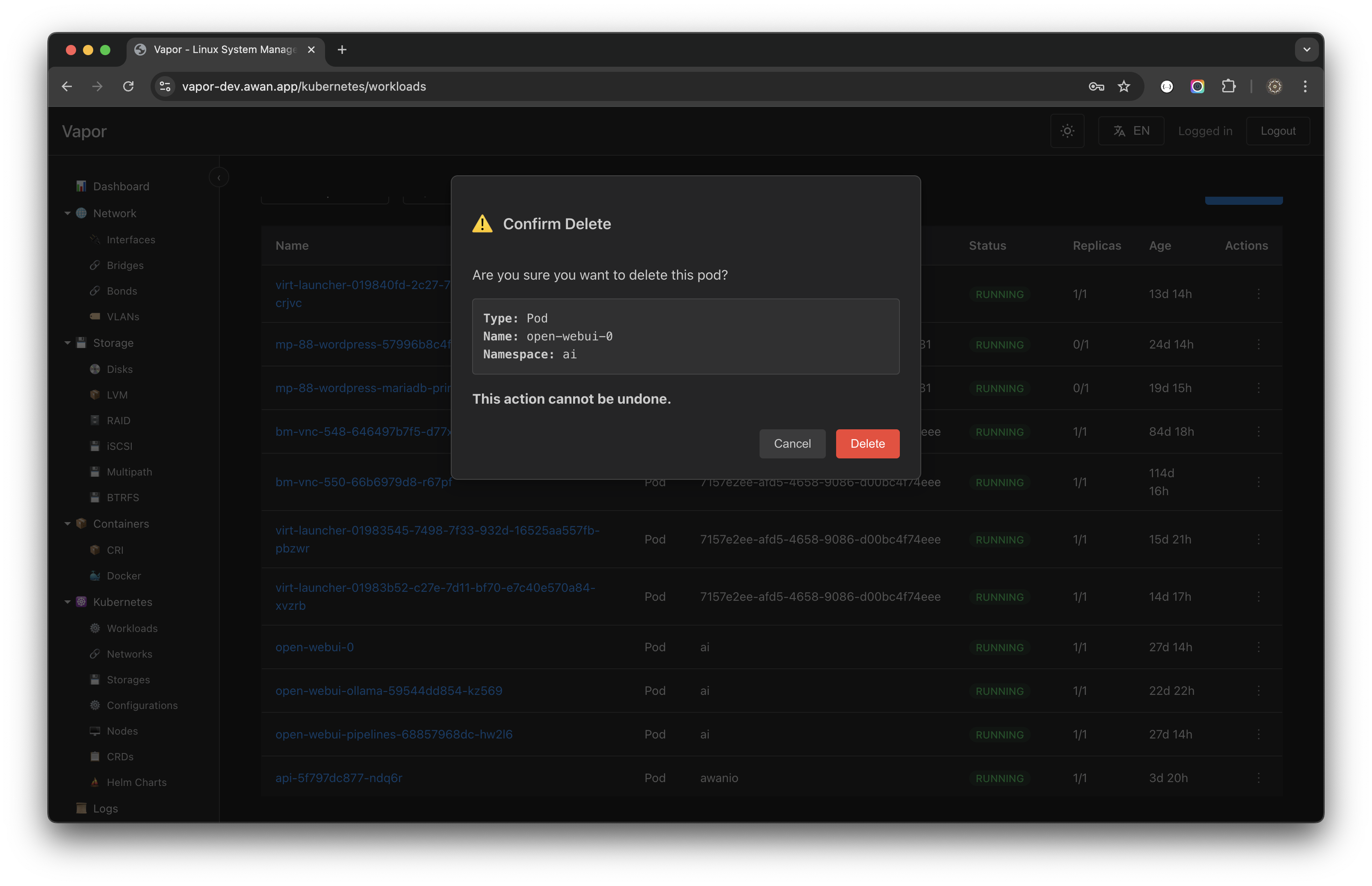
Deletion Safety:
- Confirmation dialog shows pod details
- Warning about permanent deletion
- Namespace verification
- Cancel option available
Deployments
Manage application deployments with:
Deployment Features
- Scaling: Adjust replica count
- Rolling Updates: Zero-downtime deployments
- Rollback: Revert to previous versions
- Strategy Configuration: RollingUpdate or Recreate
Creating a Deployment
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
namespace: default
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.21
ports:
- containerPort: 80Deployment Operations
- Scale: Adjust replica count up or down
- Update: Change image or configuration
- Pause/Resume: Control rollout process
- History: View revision history
StatefulSets
For stateful applications requiring:
- Stable network identities
- Persistent storage
- Ordered deployment and scaling
- Ordered termination
StatefulSet Example
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
name: mysql
spec:
serviceName: mysql
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: mysql
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: mysql
spec:
containers:
- name: mysql
image: mysql:8.0
env:
- name: MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD
value: "secretpassword"
volumeMounts:
- name: mysql-storage
mountPath: /var/lib/mysql
volumeClaimTemplates:
- metadata:
name: mysql-storage
spec:
accessModes: ["ReadWriteOnce"]
resources:
requests:
storage: 10GiDaemonSets
Deploy pods on every node:
- Log collectors
- Monitoring agents
- Network plugins
- Storage daemons
Jobs and CronJobs
Jobs
One-time tasks:
- Data processing
- Batch operations
- Maintenance tasks
CronJobs
Scheduled recurring tasks:
- Backups
- Report generation
- Cleanup operations
Networking
Services
Expose applications within the cluster:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-service
spec:
selector:
app: nginx
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 80
type: ClusterIPService Types:
- ClusterIP: Internal cluster access
- NodePort: External access via node ports
- LoadBalancer: Cloud provider load balancer
- ExternalName: DNS CNAME record
Ingresses
HTTP/HTTPS routing:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: nginx-ingress
spec:
rules:
- host: app.example.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: nginx-service
port:
number: 80Storage
Persistent Volume Claims (PVCs)
Request storage for pods:
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: mysql-pvc
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 20Gi
storageClassName: fast-ssdStorage Classes
Define storage types:
- Performance tiers
- Backup policies
- Encryption settings
- Provisioner configuration
Configuration
ConfigMaps
Store configuration data:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: app-config
data:
database.conf: |
host=localhost
port=5432
name=myapp
app.properties: |
debug=false
version=1.0.0Secrets
Manage sensitive data:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: mysql-secret
type: Opaque
data:
password: cGFzc3dvcmQxMjM= # base64 encodedHelm Chart Management
Vapor includes full Helm support:
Helm Operations
- List Releases: View all deployed charts
- Install Charts: Deploy from repositories
- Upgrade Releases: Update to new versions
- Rollback: Revert to previous releases
- Uninstall: Remove deployed charts
Installing a Helm Chart
# Example: Installing Prometheus
helm repo add prometheus-community https://prometheus-community.github.io/helm-charts
helm install prometheus prometheus-community/prometheusManaging Releases
View and manage Helm releases:
- Release name and namespace
- Chart version
- App version
- Status (deployed, failed, pending)
- Last updated timestamp
Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs)
Extend Kubernetes with custom resources:
Viewing CRDs
- List all installed CRDs
- View CRD details and versions
- Access custom resources
- Monitor CRD status
Common CRDs
- Cert-manager certificates
- Istio service mesh
- Prometheus monitoring
- Operator-managed resources
Node Management
Monitor cluster nodes:
- Resource allocation
- Pod scheduling
- Node conditions
- Taints and tolerations
Best Practices
Resource Management
- Set resource limits: Prevent resource exhaustion
- Use namespaces: Isolate workloads
- Label consistently: Easier management
- Monitor resources: Track usage patterns
Security
- Use RBAC: Role-based access control
- Secure secrets: Encrypt sensitive data
- Network policies: Control traffic flow
- Pod security: Use security contexts
High Availability
- Multiple replicas: Avoid single points of failure
- Pod disruption budgets: Control maintenance
- Liveness probes: Automatic recovery
- Readiness probes: Traffic management
Troubleshooting
Common Issues
Pods Not Starting
- Check pod events
- Review container logs
- Verify image availability
- Check resource constraints
Service Discovery
- Verify service selectors
- Check endpoint creation
- Test DNS resolution
- Validate network policies
Storage Issues
- Check PVC binding
- Verify storage class
- Review volume permissions
- Monitor disk space
Integration with CI/CD
Vapor's Kubernetes features integrate with:
- GitOps workflows
- CI/CD pipelines
- Helm charts
- Kubectl commands
Next Steps
- Explore Container Management
- Learn about API Integration
- Review Security Best Practices
